Managing Type 2 Diabetes is not just about monitoring your blood sugar levels—it’s about adopting a lifestyle that promotes overall health. One of the most effective ways to do this is through diet. By understanding and controlling what you eat, you can significantly impact your diabetes management. This blog aims to provide you with actionable insights on crafting a healthy diabetic diet that supports optimal blood sugar control.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by insulin resistance, where the body doesn’t use insulin properly. This leads to elevated blood sugar levels, which over time, can cause serious health complications. Understanding how diabetes develops and affects the body is crucial for effective management.
Risk Factors
Certain risk factors increase the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes. These include genetics, weight, inactivity, and age—factors that impact insulin resistance and blood sugar management. Identifying and understanding these risk factors can aid in early intervention and prevention.
The Role of Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance plays a pivotal role in type 2 diabetes. When your body’s cells resist insulin’s efforts to move glucose into them, blood sugar levels rise. Improving insulin sensitivity through diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes is key to managing diabetes.
The Role of Diet in Diabetes Management
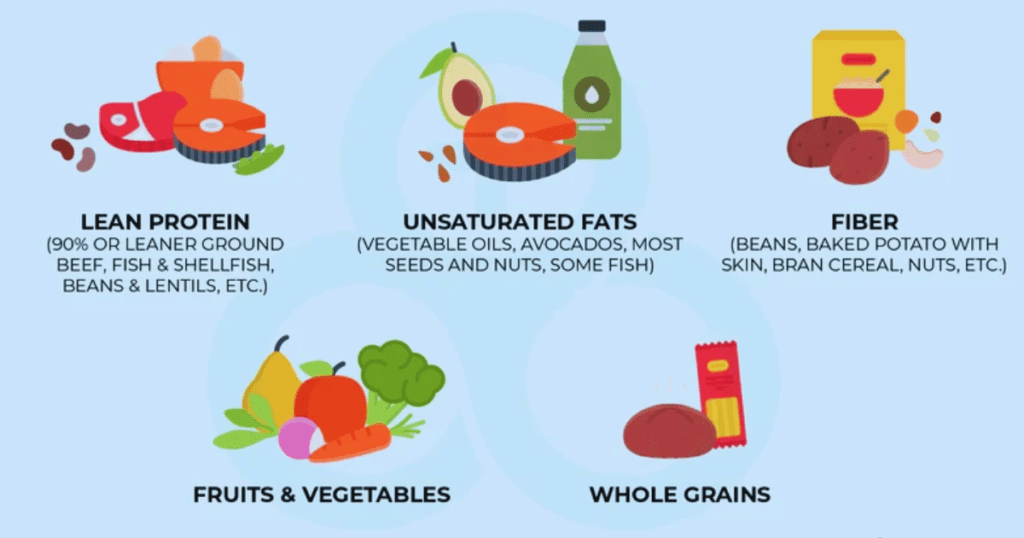
How Diet Affects Blood Sugar Levels
Diet profoundly influences blood sugar levels. Carbohydrates are the main culprits affecting blood glucose, so choosing low-glycemic index foods is vital. A balanced diet rich in fiber, proteins, and healthy fats helps maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day.
The Glycemic Index (GI)
The glycemic index ranks foods based on how they affect blood glucose levels. Foods with a low GI result in a gradual rise in blood sugar, which is beneficial for diabetes control. Incorporate low GI foods into your diabetes meal planning to help stabilize blood sugar.
Balancing Macronutrients
Balancing macronutrients is crucial in a diabetic diet. Lean proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates should form the foundation of your meals. A balanced diet ensures better blood sugar regulation and supports overall health.
Top 20 Foods to Incorporate into a Diabetes-Friendly Diet
Eating the right foods can make all the difference in managing type 2 diabetes. Here’s a list of foods that support blood sugar control and offer various health benefits:
- Leafy Greens: Low in calories and high in fiber, packed with vitamins. Recipe ideas: salads, smoothies
- Berries: Antioxidant-rich and high in fiber, excellent for diabetic-friendly fruits. Recipe ideas: smoothies, yogurt parfaits
- Nuts: Rich in healthy fats and fiber, perfect snacks for balancing blood sugar levels.
- Legumes: High in fiber and protein, great for hearty, diabetes-friendly meals.
- Whole Grains: Low GI foods like quinoa and brown rice help maintain blood sugar stability.
- Greek Yogurt: Offers probiotic benefits and high protein content, nutritious addition to your diet.
- Cinnamon: Improves insulin sensitivity, beneficial for blood sugar management.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: May help lower blood sugar levels after meals, fast fat burning supports diabetes control naturally.
- Sweet Potatoes: Rich in fiber and vitamin A, a delicious low-GI food option.
- Chia Seeds: Packed with omega-3 fatty acids and fiber, diabetic superfoods.
- Flaxseeds: Rich in fiber and healthy fats, ideal for diabetes-friendly snacks.
- Okra: Offers potential benefits in lowering blood sugar, valuable for diabetics.
- Kimchi and Sauerkraut: Probiotics and gut health benefits, support diabetes management.
- Kefir: Rich in probiotics, may aid in regulating blood sugar and enhancing gut health.
- Almonds: Good source of healthy fats and fiber, perfect for blood sugar control snacks.
- Avocados: Contain healthy fats and fiber, help stabilize blood sugar.
- Citrus Fruits: High in vitamin C and low in sugar, excellent for diabetes management.
- Tomatoes: Low GI and rich in antioxidants, versatile for diabetic diets.
- Garlic: Natural blood sugar-lowering properties, flavorful addition to recipes.
- Turmeric: Anti-inflammatory properties and potential to improve insulin sensitivity, great in natural diabetes remedies.
Foods to Limit or Avoid
Avoiding certain foods is just as important as including others. Here’s a list of foods that may interfere with managing type 2 diabetes:

Sugary Beverages
These drinks cause blood sugar spikes and should be replaced with healthier options.
Refined Carbohydrates
White bread, pasta, and rice raise blood sugar quickly; opt for whole grains instead.
Processed Meats
Increase the risk of insulin resistance and heart disease; better to choose fresh, lean meats.
Fried Foods
High in trans fats, fried foods can worsen diabetes management; baking or grilling is preferable.
Full-Fat Dairy Products
Linked to insulin resistance, it’s best to choose low-fat or plant-based alternatives.
Sugary Snacks and Desserts
High in GI and calories, these should be avoided to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Trans Fats
Found in packaged and processed foods, harmful to insulin sensitivity; alternatives are healthier fats.
Meal Planning and Preparation Tips
Effective meal planning is vital for diabetes management. Here are some tips:
Portion Control
Understanding portion sizes is crucial in preventing overeating, which can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels. By measuring and controlling the amount of food you consume, you can better manage your blood sugar and maintain a healthy weight.
Balanced Meals
Ensuring that your meals comprise a balance of macronutrients—carbohydrates, proteins, and fats—is essential for blood sugar control. A well-balanced meal can help stabilize blood sugar levels, provide sustained energy, and support overall health.
Reading Nutrition Labels
Learning to read food labels is an important skill for making diabetes-friendly choices. By understanding the nutritional content of packaged foods, you can select options that are lower in sugar, sodium, and unhealthy fats, contributing to better diabetes management.
Incorporating Variety
Incorporating a diverse range of foods into your diet ensures you receive adequate nutrients, which is vital for maintaining overall health. A varied diet can help prevent nutrient deficiencies and keep meals interesting, encouraging adherence to healthy eating habits.
Lifestyle Modifications to Complement Dietary Changes
Pair diet modifications with lifestyle changes to optimize diabetes management.
Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity is vital for managing diabetes effectively. Exercise enhances insulin sensitivity, allowing your body to utilize insulin more efficiently, which in turn helps control blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming. Incorporating strength-training exercises twice a week can also be beneficial for overall health and glucose metabolism.
Stress Management
Managing stress is crucial for anyone with diabetes, as stress can significantly impact blood sugar levels. Prolonged stress may lead to increased production of hormones like cortisol, which can raise blood glucose. Therefore, it’s essential to explore various stress-reduction techniques, such as mindfulness meditation, deep-breathing exercises, yoga, or even engaging in hobbies that bring joy and relaxation.
Sleep
Adequate sleep is an often-overlooked component of diabetes management. Poor sleep can negatively affect insulin sensitivity, making it harder for your body to control blood sugar levels. Establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a restful sleeping environment, and practicing good sleep hygiene—such as limiting screen time before bed and avoiding caffeine in the evening—can support overall health and diabetes management.
Consulting Healthcare Professionals
Regular engagement with healthcare professionals is vital for effective diabetes management. They can offer personalized advice and monitor your progress to ensure you are on the right track.
Personalized Advice
Working with a diabetes dietitian can be particularly beneficial. They can help you develop a tailored diet plan that meets your specific nutritional needs while keeping your blood sugar levels in check. This individualized approach considers your lifestyle, preferences, and any other health conditions you may have.
Regular Medical Check-ups
Continuous monitoring by your healthcare team is essential for optimal diabetes management. Regular medical check-ups allow for adjustments in medication, lifestyle, or diet as needed and provide an opportunity to address any concerns or symptoms you may experience. Your healthcare team can offer the support and guidance necessary to maintain your health and improve your quality of life.
Taking Control of Your Diabetes Through Diet
By making informed dietary choices and committing to a balanced lifestyle, you can effectively manage type 2 diabetes. Focus on a diabetes-friendly, nutrient-rich diet alongside other lifestyle changes for long-term health improvements. Remember, you don’t have to make drastic changes all at once. Small, consistent modifications can lead to significant improvements in managing your diabetes and overall well-being. Consult with your healthcare team for personalized advice and support throughout your journey towards better diabetes management. Let’s take control of our health and thrive! With the right tools and support, we can successfully manage type 2 diabetes and live a fulfilling life. So let’s continue making positive choices and prioritizing our health every day!
FAQ about Type 2 Diabetes
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way your body metabolizes sugar (glucose), an essential source of energy. In this condition, the body either resists the effects of insulin—a hormone that regulates sugar movement into your cells—or doesn’t produce enough insulin to maintain normal glucose levels.
Who is at risk for Type 2 Diabetes?
People with a family history of diabetes, those who are overweight, physically inactive, or older than 45 are at higher risk. Ethnic groups such as African Americans, Hispanic Americans, and Native Americans also have higher prevalence rates. Certain conditions like high blood pressure and polycystic ovary syndrome may also increase the risk.
Can Type 2 Diabetes be prevented?
Yes, Type 2 diabetes can often be prevented or delayed through lifestyle changes. Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and eating a balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables can significantly reduce your risk.
What are the common symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes?
Common symptoms include increased thirst and hunger, frequent urination, fatigue, blurred vision, slow-healing sores, and frequent infections. Some people may not notice symptoms early on, so regular check-ups are crucial.
How is Type 2 Diabetes diagnosed?
Type 2 diabetes is diagnosed through blood tests. The most common tests include the A1C test, fasting blood sugar test, and oral glucose tolerance test. These tests measure your blood sugar levels and help gauge how well your body is managing glucose.
What are the treatment options for Type 2 Diabetes?
Treatment often involves lifestyle changes like diet modifications, physical activity, and monitoring blood glucose levels. Medications such as Metformin are commonly prescribed, and in some cases, insulin therapy is necessary. Working closely with your healthcare provider is key to finding the right treatment plan.
How can Type 2 Diabetes affect my health if left untreated?
Uncontrolled Type 2 diabetes can lead to severe complications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage, vision problems, and increased risk of infections. Managing diabetes effectively can help prevent or delay these complications.
Can I live a normal life with Type 2 Diabetes?
Yes, with careful management, people with Type 2 diabetes can live healthy, active lives. Adopting a diabetes-friendly lifestyle, closely monitoring blood sugar levels, and maintaining regular consultations with healthcare professionals are vital for living well with diabetes.
What are the 4 stages of type 2 diabetes?
Insulin Resistance: Cells become less responsive to insulin, leading to higher blood sugar.
Pre-diabetes: Blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough for a diabetes diagnosis.
Type 2 Diabetes: Blood sugar levels are consistently high due to insufficient insulin or insulin resistance.
Diabetes Complications: Long-term high blood sugar can lead to complications like heart disease, nerve damage, and kidney problems.
Resources
- American Diabetes Association: https://www.diabetes.org/
- Mayo Clinic: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/type-2-diabetes
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/home/index.html
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview
- International Diabetes Federation: https://idf.org/
Remember, managing type 2 diabetes is a lifelong journey, so don’t get discouraged if you face challenges along the way. Stay informed, stay proactive, and continue to prioritize your health. With the right approach and support, you can successfully manage your condition and live a fulfilling life.
Thank you for reading! We hope this guide has provided helpful information and tips for managing type 2 diabetes through

